There are several ways to limit or restrict WordPress admin access by IP address.
Add some code to your wp-config file to restrict access to the WordPress admin area. Here are the steps:
- Log in to your website’s server using an FTP app like Filezilla or the file manager in your hosting control panel.
- Locate the wp-config file in the root directory of your WordPress installation.
- Download the wp-config.php file to your computer and open it in a text editor.
- Add the following code to the wp-config.php file:
/* Add any custom values between this line and the "stop editing" line. */
$ip_allowlist = [
159.223.78.3,
193.56.29.113,
178.62.113.151,
80.76.51.210,
193.201.9.202,
45.227.254.22,
];
$ip = $_SERVER['REMOTE_ADDR'];
if ( preg_match( '/(wp-login.php)/', $_SERVER['REQUEST_URI'] ) ) {
$ip_found = in_array( $ip, $ip_allowlist, true );
if ( ! $ip_found ) {
// Check if this IP is in CIDR
foreach ( $ip_allowlist as $_cidr ) {
if ( strpos( $_cidr, '/' ) !== false ) {
$_ip = ip2long( $ip );
// expand the range of ips.
list ( $_net, $_mask ) = explode( '/', $_cidr, 2 );
// subnet.
$_ip_net = ip2long( $_net );
$_ip_mask = ~( ( 1 << ( 32 - $_mask ) ) - 1 );
if ( ( $_ip & $_ip_mask ) === ( $_ip_net & $_ip_mask ) ) {
$ip_found = true;
break;
}
}
}
}
if ( ! $ip_found ) {
header( 'HTTP/1.0 403 Forbidden' );
exit;
}
}
Replace xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx with the IP address that you want to allow access to the WordPress admin area. If you have multiple IP addresses, you can add one per line.
- Save the changes to the wp-config.php file.
- Upload the modified wp-config.php file back to your server, overwriting the original file.
After following these steps, only the specified IP addresses will have access to the WordPress admin area. Any other IP addresses trying to access the admin area will receive a 403 Forbidden error.
Alternatively, you can use the plugin Traffic Jammer that I wrote.
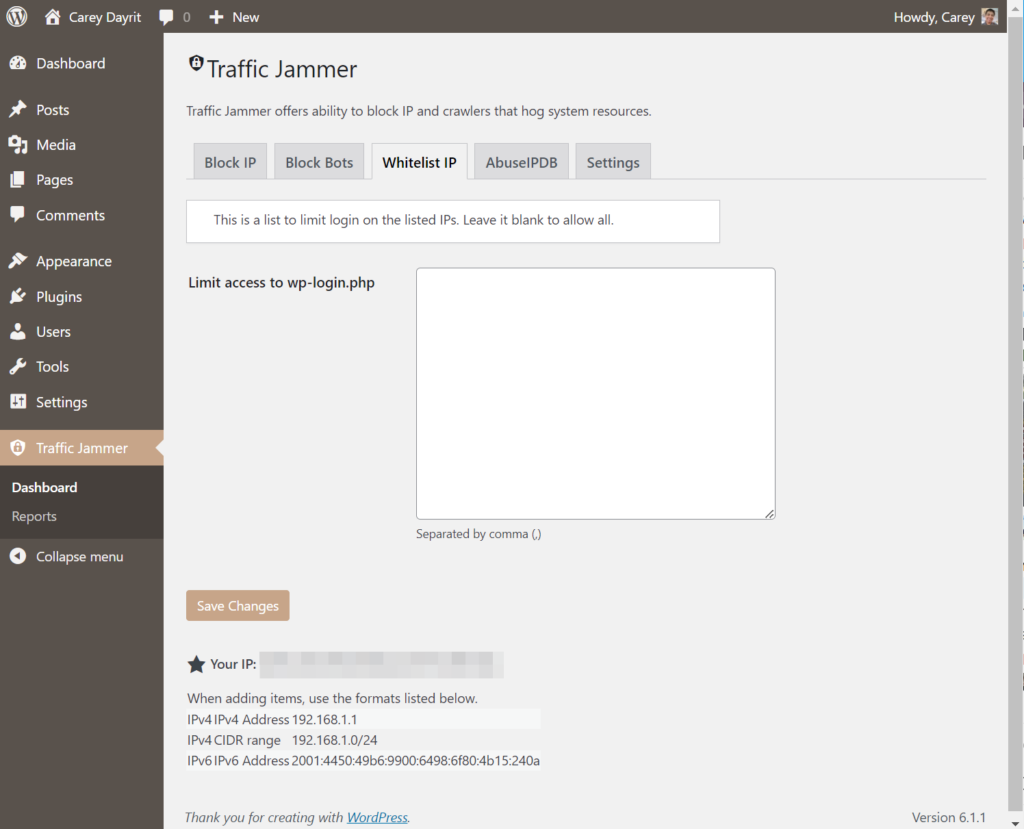
There is also a wp-cli command that is included in the plugin, here are the commands:
wp jam trust <IP> – add IP to the allowed list
wp jam untrust <IP> – remove IP from the allowed list
wp jam trustall – clear all limits
This plugin can also be used on the Pantheon terminus command, the plugin is very compatible with Pantheon no need to assume write access or symlinks to properly install the plugin.
terminus wp <sitename>.<env> -- jam <commands>